本地化是指在游戏内窗口实际呈现给玩家的文本,如事件、菜单、武器、故事等。本地化文件以.yml的格式保存在localisation/folder路径底下,且以UTF-8-BOM的格式编码。.yml文件的命名惯例是<文件名>_l_<语言名>.yml,其中<文件名>为这组本地化的名字,而<语言名>为本地化的目标语言。目前支持的语言有葡萄牙语(braz_por),英语(english),法语(french),德语(german),波兰语(polish),俄语(russian),西班牙语(spanish),以及简体中文(simp_chinese)。
实用指令:
reload text – 重新加载本地化目录。 switchlanguage l_english – 切换语言并重新加载本地化目录。
创建本地化文件
- 在模组的根文件夹(注意不在common里)创建一个名为“localisation”的文件夹。注意,在某些别的paradox游戏里用的可能是美式拼写、带有z的“localization”。
- (可选)在“localisation”文件夹中创建对应语言的子文件夹。这有助于管理,但不是必需的。
- 群星的本地化文件是用UTF-8-BOM编码的。UTF-8-BOM是唯一可用的编码方式,就算用UTF-8编码也会导致群星无法解析从而不能使用。
- 正确编码的最简单做法是复制一个现成的群星.yml文件,再直接对其进行编辑。
- 作为替代,你也可以创建一个标准的空白文本文档,再以UTF-8-BOM编码保存它。类似Notepad++和Visual Studio Code这样的文本编辑器能让你手动将文件保存为UTF-8-BOM编码格式。
- 文件名必须以“_l_<语言名>”结尾,否则无法被读取。
- 任何本地化文件的第一行都必须是
l_<language>:,否则无法被读取。 - 范例文件名:
mod_buildings_l_english.yml
将YML文件命名为与一个原版YML文件相同会导致原版被覆盖。这么做并不推荐, 除非你打算改写文件内(几乎)所有的条目。本地化条目可以通过保存到“Replace”文件夹以单独被覆盖,详见overwrite section.
遗憾的是,游戏并没有适配模组的语言回滚功能。这意味着当本地化键值缺失时,键值会直接以文本形式呈现。因此,对应的做法是先直接把英语文件复制到其他所有语言里(改成合适的标题)。
文件编码
- 使用一个文本编辑器打开YML文件。推荐使用类似Notepad++和Visual Studio Code 这样的编辑器,如果上述软件不可用的话,普通的记事本也行。
- 将文件转码成UTF-8-BOM的格式。
- 使用Notepad++时,前往菜单栏,打开编码 界面。
- 使用Visual Studio Code时,前往右下角并点击编码(默认为
UTF-8),再点击保存编码。作为替代,也可以通过改变设置来让VSC默认以UTF-8-BOM 格式生成YML文件。 - 使用记事本时,前往另存为...,改变编码并保存文件。
- 如果列出来的选项中同时有UTF-8 和UTF-8 with BOM(或相似的名称),选用UTF-8-BOM。
- 如果列出来的选项中同时有UTF-8 和UTF-8 without BOM(或相似的名称),选用UTF-8。【译注:即一定要带BOM】
本地化键值
l_<语言名>: localisation_key_1: "文本1" localisation_key_2: "文本2"
每个单独的本地化条目被称为“键值”,位于冒号的左侧,是指向本地化文本的实际代码。而游戏内显示的文本则位于冒号的右侧,包夹在双引号("")里。冒号是分隔符。
- 原版文件中紧接在冒号后面的数字可以被忽略,那是Paradox内部用于跟踪翻译用的。[1]
- 在出现任何本地化键值之前,文件必须先包含
l_english:(或其他语言的相等形式)。 l_english:(或相等)之后的所有条目必须以空格开始(空格或tab都行)。- 所有要在游戏内显示的文本都被双引号所包裹。想在游戏内显示双引号的话,请在双引号前面加上反斜杠(例如:
text \"name\")。 - 注意后面这些unicode字符在本地化文件中是不可用的,会生成一个“?”:
„ “ ‚ ‘ – ” ’ … —
覆盖原版文本
想要覆盖原版本地化键值(或其他模组的键值)时,在你的“localisation”文件夹底下创建一个名为“replace”的文件夹。该文件夹中的本地化文件的读取比其他所有本地化文件都晚,能覆盖掉任何重复的键值。这样做可以避免覆盖所有本地化文件,每个键值条目会单独被最后加载的文件所覆盖。不通过“replace”文件夹来覆盖本地化是可行的,但并不可靠。
Bracket Commands
Bracket commands (scoped localization statements) are enclosed in square brackets ([ ]), start with a primary scope, end with a text retrieval, and can have one or more secondary scopes in between. The fields are separated by periods (.). Text retrievals can be predefined (as per examples below), can mention Variables defined in the scope, or can be a scripted_loc (see common/scripted_loc/ files for examples). When writing "scripted_loc" entries, it’s important to note that these entries cannot themselves use bracket commands (i.e., a scripted_loc that includes [Root.GetName] will literally print [Root.GetName]).
Note: if you want to use loc commands e.g. log = [This.GetName] in a scripted effect or trigger, you have to write it \\[This.GetName] or it will bug out (at the latest the second time you use one in the effect).
In most cases, it is also possible to get the value of variables with '[Scope.my_variable]' and saved dates with '[Scope.my_date_flag]'.(since 3.1)
Two consecutive opening square brackets '[[' will escape it, making a single square bracket show up in text instead, i.e. '[[example]' in loc will display as '[example]' in-game.
There are also several unscoped commands: GetDate, GetMidGameDate, GetLateGameDate, GetYear, LastKilledCountryName.
Following list is only a part of hardcoded scoped localization commands (it also does not include any scripted locs). A more complete list of commands can be found at Stellaris\logs\script_documentation\localizations.log.
Primary Scopes
| Command | Example usage | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Root | [Root.GetName] | The event’s root scope |
| This | [This.GetName] | The current scope |
| From | [From.From.GetName] | The calling event’s root scope. For events further back in the call stack, From can also be used as a secondary scope |
| Prev | [Prev.From.GetName] | The previous scope. It is not obvious to me what Prev.From points to, but some project descriptions use it |
| <event target tag> | [mytarget.GetName] | Event target tags are used without preceding them with event_target: in localisation
|
| Diplomatic Promotions | ||
| Actor | [Actor.GetAllianceName] | Used in diplomatic response messages. The faction initiating an action |
| Recipient | [Recipient.GetName] | Used in diplomatic response messages. The faction targeted by the action |
| Third_party | [Third_party.GetName] | Used in diplomatic response messages. A third party involved in the action |
Secondary Scopes
| Command | Example usage | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Country Promotions: Capital Ruler Heir Species Federation | ||
| Capital | [Root.Capital.GetName] | The capital of the current country or sector |
| Leader | [Root.Leader.GetName] | The leader of the current scope (fleet, country, federation, pop faction, first contact, espionage operation, spy network, sector) |
| War Promotions | ||
| MainAttacker | [This.MainAttacker.GetAllianceName] | The main attacker of the current scope (must be used in a war scope), used in war name formats |
| MainDefender | [This.MainDefender.GetSpeciesName] | The main defender of the current scope (must be a war scope), used in war name formats |
| Planet Promotions: Owner System MoonOf Sector | ||
| Owner | [Root.Owner.GetName] | The current scope’s owner |
| System | [Root.System.GetName] | The system where the primary scope is located |
| Planet | [Root.Planet.GetName] | The planet where the current scope is located (pop, army, archaeological site, deposit, megastructure) |
Text Retrieval
| Command | Example usage | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| GetAdj | [Root.GetAdj] | The adjective associated with the current scope |
| GetAdjective | [Root.GetAdjective] | The adjective associated with the current scope |
| GetAllianceName | [This.MainAttacker.GetAllianceName] | The name of the alliance the current scope belongs to |
| GetControllerName | [Root.GetControllerName] | Name of the current controller (known to work on planets) |
| GetClassName | [Root.GetClassName] | Name of the current planet class |
| GetFleetName | [Root.GetFleetName] | The name of the fleet associated with the current scope |
| GetHeirName | [Root.GetHeirName] | The name of the current heir |
| GetHeirTitle | [Root.GetHeirTitle] | The title of the current heir |
| GetHomeWorldName | [Root.GetHomeWorldName] | The name of the home world of the current scope |
| GetLeaderName | [Root.GetLeaderName] | The name of the leader associated with the current scope |
| GetName | [Root.GetName] | The name associated with the current scope |
| GetFirstName | [Root.GetFirstName] | The name first associated with the current scoped leader |
| GetSecondName | [Root.GetSecondName] | The second name associated with the current scoped leader |
| GetAge | [Root.GetAge] | The age of the scoped leader |
| GetNamePlural | [Root.GetNamePlural] | The plural name associated with the current scope (must be a species) |
| GetNebula | [Root.GetNebula] | (unknown) |
| GetOwnerName | [Root.GetOwnerName] | Name of the current owner |
| GetPersonalityName | [Root.GetPersonalityName] | Get the name of the current AI personality |
| GetPlanetMoon | [Root.GetPlanetMoon] | "planet" or "moon" depending on whether the current scope is a planet or moon |
| GetPlanetMoonCap | [Root.GetPlanetMoonCap] | "Planet" or "Moon" depending on whether the current scope is a planet or moon |
| GetPopFactionName | [Root.GetPopFactionName] | The name of the currently scoped pop’s faction |
| GetRandomSpeciesSound | [Root.GetRandomSpeciesSound] | A sound chosen randomly from a list of sounds associated with current scope’s species |
| GetRegnalName | [Root.GetRegnalName] | The regnal name of the current scope |
| GetRulerName | [Root.GetRulerName] | The name of the ruler associated with the current scope |
| GetRulerTitle | [Root.GetRulerTitle] | The title of the ruler associated with the current scope |
| GetSpeciesAdj | [Root.GetSpeciesAdj] | The adjective for the species of the current scope |
| GetSpeciesClass | [Root.GetSpeciesClass] | The class to which the species of the current scope belongs |
| GetSpeciesClassPlural | [Root.GetSpeciesClassPlural] | The plural of the current scope’s species’ clas |
| GetSpeciesMouthName | [Root.GetSpeciesMouthName] | The word for the current scope’s species’ mouth |
| GetSpeciesName | [Root.GetSpeciesName] | The name of the current scope’s species |
| GetSpeciesNameCompliment | [From.GetSpeciesNameCompliment] | A compliment using the current scope’s species |
| GetSpeciesNameInsult | [From.From.GetSpeciesNameInsult] | An insult using the current scope’s species |
| GetSpeciesNamePlural | [This.GetSpeciesNamePlural] | The plural of current scope’s species’ name |
| GetSpeciesNamePluralCompliment | [Root.SpeciesNamePluralCompliment] | A compliment using the plural of the current scope’s species’ name |
| GetSpeciesNamePluralInsult | [From.SpeciesNamePluralInsult] | An insult using the plural of the current scope’s species’ name |
| GetSpeciesHandName | [From.GetSpeciesHandName] | The word for the current scope’s species’ hand |
| GetSpeciesMouthName | [From.GetSpeciesMouthName] | The word for the current scope’s species’ mouth |
| GetSpeciesOrganName | [From.GetSpeciesOrganName] | The word for the current scope’s species’ internal organ |
| GetSpeciesSpawnName | [Root.GetSpeciesSpawnName | The word for the children of the current scope’s species |
| GetSpeciesSpawnNamePlural | [Root.GetSpeciesSpawnNamePlural | The plural word for the children of the current scope’s species |
| GetStarName | [Root.Capital.GetStarName] | The name of the star where the current scope is located |
| GetHerHim | [admiral.GetHerHim] | Prints 'her' or 'him' based on the character’s gender. |
| GetSheHe | [abducted_leader.GetSheHe] | Prints 'she' or 'he' based on the character’s gender. |
| GetSheHeCap | [abducted_leader.GetSheHeCap] | Prints 'She' or 'He' based on the character’s gender. |
| GetHomeWorldName | [Root.GetHomeWorldName] | The home world name of the selected country |
| GetHerHis | [admiral.GetHerHis] | Prints 'her' or 'his’ based on the character’s gender. |
| GetHerHisCap | [admiral.GetHerHisCap] | Prints 'Her' or 'His’ based on the character’s gender. |
| LastKilledCountryName | [LastKilledCountryName] | Prints the name of the last killed country. |
- Added localization commands with Patch 3.1.
GetSpeciesFossilName GetSpeciesFossilNamePlural GetSpeciesRemnantName GetSpeciesRemnantNamePlural Species GetFossilName GetFossilNamePlural GetRemnantName GetRemnantNamePlural
Color Codes
Color codes start with § (Windows users Keypad shortcut: ALT+0167), which is followed by a single character specifying the color to be used until another color code is detected, or the end of the string: §!. Within a $ command, the color for a displayed variable (not string definition, s. below $ Codes) may also be specified by preceding the closing $ with | and the color code character: $AGE|Y$
It is also possible to change the text color in game by adding a DC1 UTF-8 character to a color code letter. Please note that doing so may unintentionally color subsequent text if the color is not changed to default at the end.
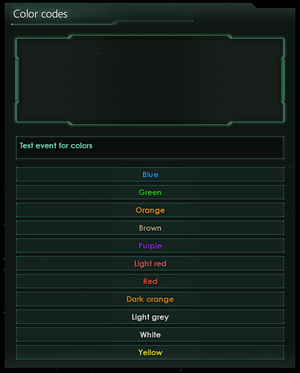
§RR§Sa§Hi§Yn§Gb§Bo§Mw§! will be displayed as:Rainbow
| Code | Color | Vanilla Use |
|---|---|---|
| W | White | Diplomatic Attitudes |
| T | Light grey | Standard color of all text |
| L | Brown | Lore, back story, role playing elements |
| P | Light red | Highlighting of Aggressive text in descriptions and event text |
| R | Red | Negative modifiers |
| S | Dark orange | Subtle highlighted text |
| H | Orange | Highlighted text |
| Y | Yellow | Sub-optimal or Neutral modifiers |
| G | Green | Positive modifiers |
| E | Teal | Large chunks of text |
| B | Blue | Event effects that affect pops |
| M | Purple | Rare technologies |
| ! | Default | Return to color before last color change |
$ Codes
$ is used to delimit strings (or variables) defined elsewhere to be expanded in the current string, or system statistics in GUI elements.
Number Formatting
The | character can also be used to format numbers. $VALUE|*x$ will format VALUE to x decimal places.
# EXAMPLE = 100 "$EXAMPLE|*0$" # 100 "$EXAMPLE|*1$" # 100.0
£ Codes
£ codes are used for the names of various system stats, including energy, minerals, influence, and the three research categories (engineering, physics and society.) More exist than those listed here, such as £ship_stats_hitpoints\armor\shield£, £fleet_template_size£, and £trigger_yes\no£ among others. Search the '£' character using something like Notepad++'s Find in Files feature to find something specific. Remember that £ codes must surround the tag you're inserting, i.e. £energy£. (Windows users without the pound symbol on their keyboards can use Alt + 0163.)
It also supports the multiple frames (if the source sprite has them), i.e.: £leader_skill|3£ will render an icon of chosen skill level.
£ Custom Icons
You can create custom text icons to appear in game exactly like those above, by saving an icon in <root>/gfx/interface/icons/text_icons. Standard text icons are 16x16 pixel .dds files. In order to reference your icon in text, you will need to define it in the same way you define event pictures. Save a text file as .gfx in <root>/interface/ Define any custom modifiers as shown below:
spriteTypes = {
spriteType = {
name = "GFX_text_worker_produces_mult"
texturefile = "gfx/interface/icons/text_icons/mod_planet_jobs_worker_produces_mult.dds"
}
You can link multiple icons by making separate spriteType = blocks. All of these should be within one larger spriteTypes = (with an s) block.
The name must be prefixed GFX_text_. However, to reference this custom icon in localisation, use £worker_produces_mult£ (without the prefix) and it will appear alongside in game text.
Slash-Based Codes
The two slash-based codes available are \n and \t.
\n is the equivalent of pressing the Enter key and starting a new line, unless it is inside one of the above codes.
\t places a tab.
Backslashes can also be used to treat special characters as text characters, for example \" will make the string contain a quotation mark, instead of closing it off.
Style Guide
Vanilla events, modifiers and all other type of localization follows punctuation and capitalization guidelines. The following table highlights some of the rules employed in the vanilla English localization, allowing custom content to blend in more seamlessly. The table is by no means comprehensive, but instead should serve as a quick cheat-sheet for the most common type of strings. The number given for Character Limit is not a hard limit. Depending on the location, exceeding the limit might cause the text to be cut off, completely break the UI, or just look ugly and out of place.
| Location | Capitalization | Punctuation | Character Limit | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event Names | Title Case | None | 50 | "Exotic Woodwind" |
| Event Descriptions | Sentence case | Standard | 2000 | "Music has taken many forms among the beings we have encountered since leaving [Root.GetHomeWorldName], and the methods and preferences continue to baffle us. Sometimes alien […] Whatever this instrument is, it’s unlike any of our own." |
| Event Options | Sentence case | Terminal punctuation | 70 | "An excellent time to learn more about their culture.", "Let us be careful and study this instrument.", "The colony is part of our future. It stays." |
| Names for Traits/Modifiers/Buildings/Ethics/etc. | Title Case | None | 30 | "Building Cost", "Massive Crater", "Very Strong" |
| Description for Traits/Modifiers/Buildings/Ethics/etc. | Sentence case | Standard | 200 | "The impact site of the meteorite which brought Lithoids to this planet.", "Members of this species possess a strength that almost defies the laws of physics." |
| UI Buttons | Sentence case / Title Case | None | Depends on UI | "Withdraw" |
| UI Alerts | Title Case | None | Depends on UI | "Relic Activation Available" |
References
| 帝国 | 帝国 • 思潮 • 政府 • 国民理念 • 起源 • 承诺 • 议程 • 传统 • 飞升天赋 • 法令 • 政策 • 遗珍 • 科技 • 自定义帝国 |
| 人口 | 岗位 • 派系 |
| 领袖 | 领袖 • 领袖特质 |
| 物种 | 物种 • 物种特质 |
| 行星 | 行星 • 行星特征 • 轨道矿藏 • 建筑 • 区划 • 行星决议 |
| 星系 | 星系 • 恒星基地 • 巨型结构 • 虫洞 • 星门 • 地图 |
| 舰队 | 舰队 • 舰船 • 部件 |
| 地面战 | 陆军 • 轰炸姿态 |
| 外交 | 外交 • 联邦 • 星海共同体 • 评价修正 • 宣战理由 • 战争目标 |
| 事件 | 事件 • 异常现象 • 特殊项目 • 考古遗址 |
| 游玩 | 游玩 • 定义 • 研究 • 经济 • 游戏开局 |
| 动态修改 | 动态 • 指令效果 • 触发条件 • 作用域 • 修正 • 变量 • AI |
| 媒体/本地化 | Maya 导出器 • 图形 • 肖像 • 旗帜 • 事件图片 • 界面 • 图标 • 音乐 • 本地化 |
| Other | 控制台命令 • 存档编辑 • Steam 创意工坊 • 模组制作教程 |